By Rebecca Schmid
Few operas in history have gripped the human psyche to the same extent as Don Giovanni. Pushkin, Kierkegaard, and Bernard Shaw count among the literary figures to have written their own account of the daemonic seductor since Mozart and Da Ponte staged their ‘drama giocoso,’ a tragi-comedy, in Prague. Since the 19th century, some champions of the work have further added to the opera’s moral ambiguity by excluding the final sextet, “Questo é il fin di chi fa mal/e de’ perfidi la morte/alla vita è sempre ugual” (this is the end for evildoers/death and life are the same for the villainous) after Don Giovanni is sent to hell. Meanwhile, his female conquests have been increasingly interpreted as consenting perpetrators of his sexual games rather than just victims and continue to provide stage directors with ample fodder. Robert Carsen, in his new production for La Scala last December, sets the Commendatore’s murder by Don Giovanni in the chambers of Donna Anna (Anna Netrebko), leaving her white slip covered in blood as she holds her father’s dead body on the same bed where she frolicked with the murderer. In the final scene, the accursed aristocrat reemerges from hell puffing on a cigarette while his avengers descend into infernal smoke.
Carsen’s vision was supposed to travel to Berlin this month as a guest production of the Staatsoper until it emerged that it would be impossible to adapt sets to the company’s current home in the Schiller Theater (the company’s 18th-century headquarters on the Boulevard Unter den Linden are currently undergoing renovation, recently delayed—again—until 2015). In another strange twist, La Netrebko, the highlight of a live screening that will be broadcast to an outdoor plaza, announced in May that she would withdraw in order to make time for her son. The Swedish soprano Maria Bengtsson was whisked in and Claus Guth’s 2008 production, mounted during Staatsoper Intendant Jürgen Flimm’s tenure at the Salzburg Festival, quietly slated as a replacement. The star appeal was not entirely lost as Netrebko’s husband Erwin Schrott remained on the roster as Don Giovanni’s sidekick, Leporello, while the original Zerlina (Anna Prohaska), her Masetto (Stefan Kocan) and Don Ottavio (Giuseppe Filianoti) provided continuity for an event that has been touted as a highlight of the season.
The Guth staging, seen at its German premiere on June 24, takes a dark, pseudo-cinematic approach to the opera, confining the action to the middle of a dark forest with a rusty bus stop serving as the only manmade shelter. The curtain opens to a beer-chugging, ex-convict like Leporello while Donna Anna rips off the Don’s shirt in the background. In the showdown with the Commendatore, Don Giovanni is shot in the stomach with a plastic gun and walks around through the remainder of the opera with an open wound. During Donna Anna’s aria “Non mi dir,” he has already become a specter. Meanwhile, a business-like Donna Elvira chases after her one-time husband in heels, gets stoned out of her mind with Leporello, and lies on the forest floor with the dying anti-hero during her aria “Mi tradi.” In the first act, Zerlina and her bridesmaids emerge like wood nymphs in the thick of what appear to be real pines (sets and costumes by Christian Schmidt) before the stage turns to reveal a tree swing that will serve as Don Giovanni’s seduction grounds. The rotating stage spins at its fastest when Donna Anna and Don Ottavio pull up in a sedan, although they are ultimately as damned to roaming the forest as much as any other character.

(c) Monika Rittershaus
While it is hard to deny the poetic weight of setting Don Giovanni in the woods—the opening to Dante’s Inferno, “Mi ritrovai per una selva oscura” ‘I found myself in a dark forest’ is the first thing that comes to mind—the production is mired in Regie gimmicks that undermine its psychological depth. Staring at tree trunks for two full acts also proved monotonous. Guth omits the final sextet, leaving Don Giovanni to fall into the earth after the Commendatore returns to a wintry forest (further emphasizing the notion of a terrestrial hell in which the characters cannot find the way toward redemption), yet scenes such as Don Giovanni and Leporello roasting marshmallows and the senseless presence of immaculate, bourgeois dressed characters in the brambles linger irritatingly within the director’s otherwise morbid vision. To be sure, his concept is fully in keeping with the opera’s legendary blend of comic and tragic elements, and his surrealist take on Don Giovanni’s existence, trapped somewhere between life and death, could not be more dead-on in literary terms, yet the production demands a level of intellectual engagement that supersedes its theatrical appeal.
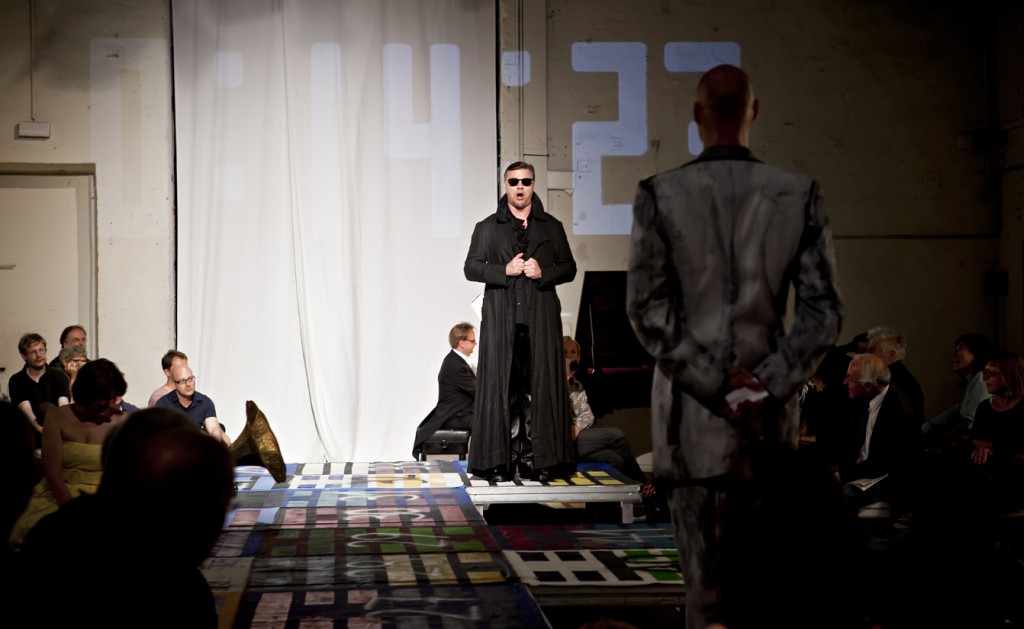
Nevertheless, Guth was blessed with a cast that largely rose above the quixotic circumstances vocally and theatrically. The audience hardly seemed to miss Netrebko as Bengtsson, a statuesque blonde with natural allure, portrayed the distraught Donna Anna with creamy tones and fine attention to dramatic nuance. Her voice was tearful in opening stanzas of “Non mi dir,” kept painfully slow by Music Director Daniel Barenboim, while she revealed unblemished strength in her swift declaration that heaven may someday forgive her. As Don Giovanni, Christopher Maltman evoked more of a modern playboy than an irresistibly virile predator, yet his high-lying baritone warmed up to give a fine rendition of his aria “Deh vieni alla finestra,” and his fear was vividly credible in the final scene. Schrott nearly stole the show as the riotous buffoon and manipulator Leporello, his booming bass and excellent Italian diction carrying magnetically in the dry acoustics of the Schiller Theater.
It is almost unfair to cast Elvira, often considered a mezzo role, with a soprano as eloquent as Dorothea Röschmann, and yet her acting skills do not always rise to the same level. While her rich tone and technical polish were the vocal stand-out of the evening, her presence more easily called to mind the countess in Le Nozze di Figaro, which she sang earlier this season, than Don Giovanni’s brash consort. As Zerlina, Prohaska (Musical America’s current “New Artist of the Month”) lived up to her usual standards of musical and thespian excellence, effortlessly singing through “La ci darem la mano” as she pumped herself on a swing. Kocan was a convincingly exasperated Masetto, although his voice retains a thick Slavic quality that interferes with the demands of singing in Italian. By contrast, Filianoti, in the role of Ottavio, cultivates a flexible technique that was ideal for the coloratura runs of the aria “Il mio tesoro,” yet his nasal timbre lacks body. He also failed to remain in time with Barenboim on more than one occasion. Ukranian Bass Alexander Tsymbalyuk was an imposing, expressively full-voiced Commendatore.
Barenboim led the Staatskapelle in a performance that never lacked dynamic shape and dramatic purpose, sensitively accompanying the singers at all times with great emotional depth, yet his tempo relations in Mozart were occasionally perplexing. The second half of “La ci darem la mano,” “Andiam mio bene” was twice as fast as the opening. The orchestra, despite its rich, Germanic sound, is also not terribly flattered by the acoustics of its current home, and its attacks could be rounder. Despite the odds stacked against this production, Barenboim proved that his ensemble is the best in town for Mozart operas, even if the composer is rolling is in his grave as Don Giovanni continues to wander the forest.
The production runs through July 6.

(c) Monika Rittershaus
Out at Friedrich the Great’s old stomping grounds…
The city of Potsdam is currently inundated with tributes to the tercentenary of Friedrich the Great, from Das Musical Friedrich to an exhibit of personal items entitled Friederisiko that stretches from the rococo palace Sanssouci to the Neue Palais, built at the end of the Seven Years’ War. While the 18th-century Prussian king may be best remembered for an aggressive military campaign that annexed parts of modern-day Poland and the Czech Republic in an escalating power struggle with the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the ‘enlightened despot’ was also a great patron of the arts. A flutist and amateur composer who penned 100 sonatas and four symphonies, Friedrich included C.P.E. Bach and Quantz among his court musicians; enjoyed a legendary if tumultuous friendship with Voltaire; and, fittingly for his time, favored the French language above German. Homages to “Old Fritz,” as he has been nicknamed, have extended to a new album released by Berlin Philharmonic Principal Flutist and soloist Emmanuel Pahud, Flöten König. The Swiss musician even dressed up earlier this season on the grounds of Sanssouci.
Potsdam’s annual Musikfestspiele (June 9-24) similarly seized upon the opportunity to transform city grounds into a courtly celebration, including a “Sanssouci Prom Concert” in the garden of the Neue Palais and ensembles as such as the Freiburger Baroque Orchester and the Orchestra of the Age of the Enlightenment in baroque and classical repertoire. The festival also included a “picnic concert” for the first time this year. The setting on Potsdam’s Freundschaftsinsel, a picturesque botanical garden nestled quietly away from the post-war architecture surrounding the main station just minutes away, proved a fitting escape for the occasion, replete with a couple in 18th-century garb pushing a tram that carried a baby anachronistically sucking a pacifier. Locals festively spread out their blankets and picnic fare, some including white tablecloths and prosecco on ice with an eye to winning the competition that was underway for “most inventive arrangement” (Potsdam, while only an hour away from Berlin and Friedrich’s summer getaway of choice, maintains its own brand of provincial flair).
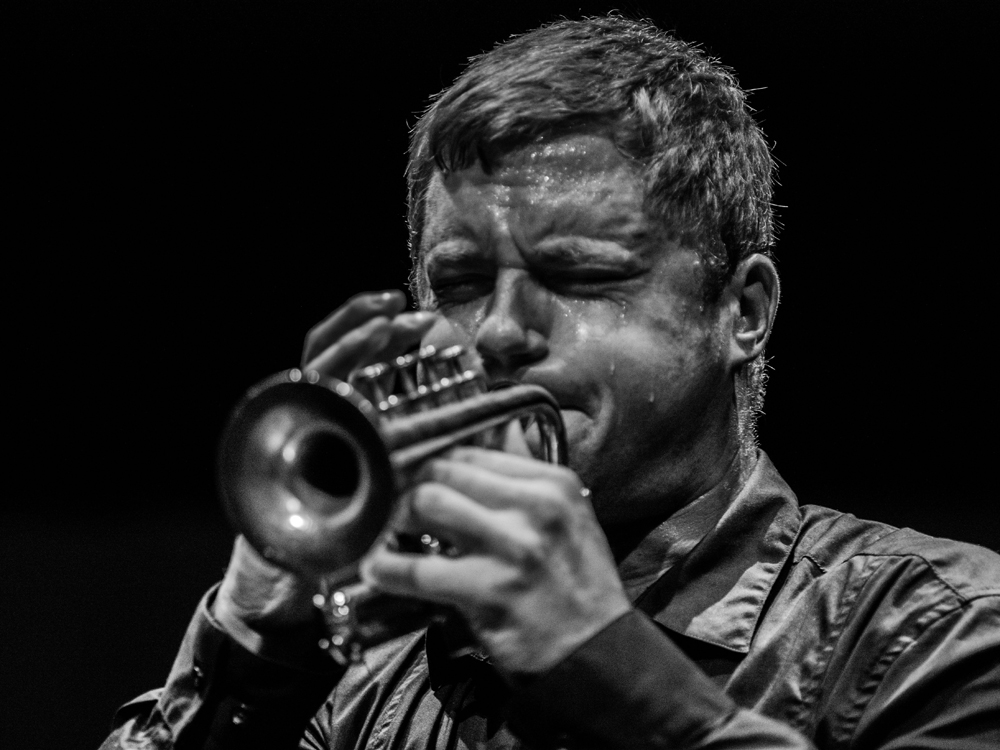
The opening concert, however, represented a decidedly non-continental take on celebrations for the Flute King, featuring the band Fine Arts Brass in an all-British program. As both a visiting journalist from a U.K. publication and one of the group’s members individually commented, it felt “surreal.” The concert fell just on the heels of the Jubilee Weekend in England, and the brass band naturally included an arrangement of Handel’s Water Music. The group’s leading trumpeter Simon Lenton, moderating between numbers with a refreshing blend of humor and informative material, joked that the German native was “England’s finest composer.” Yet the program ranged from arrangements of Dowland and Purcell to a suite by Anthony Holborne that is usually performed for Christmas and Farewell to Stromness by Peter Maxwell Davies, living proof in his position as “Master of the Queen’s Music” that the art of patronage has not died.
In conversation with the festival’s Artistic Director Andrea Palent, it emerged that the event was partly modeled after “Last Night of the Proms,” which moves from the concert hall out into Hyde Park and other outdoor venues. She also mentioned the 18th-century tradition of “pleasure gardens,” which according to Palent spread its influence throughout Europe in Friedrich’s time (although the fact remains that he was Francophile). Palent also grounded the concept in a more general principle of the Enlightenment as championed by figures such as Rousseau—“back to nature”—saying that she hoped the outdoor setting would affect listeners on a sensual as well as intellectual level.
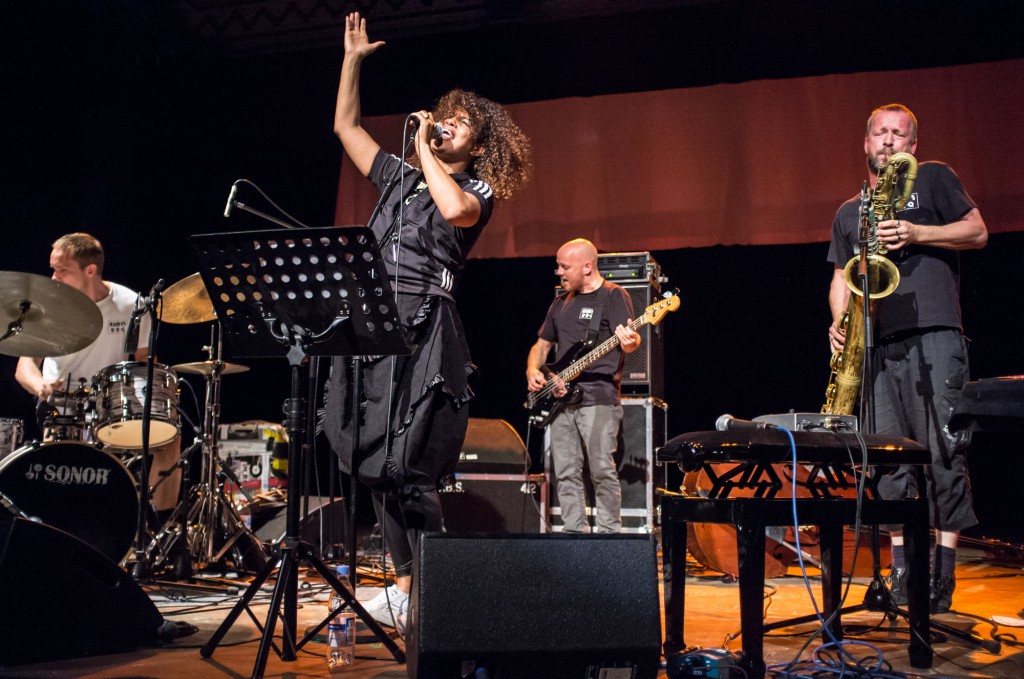
As the Meccore Quartet, a young group of Polish musicians, performed from string quartets by Haydn, Mozart, and Mendelssohn during the second part of the program, the music indeed served to heighten the sensory experience of sitting on the lawn and breathing the summer air rather than become an isolated spectacle. While one of the violinists mentioned afterwards that they had been concerned about acoustics, the music felt as if it were meant to be played in this setting, which in fact camouflaged technical and dynamic details that would have been more apparent to a critic’s ear in the concert hall. In an age of technological oversaturation, the event proved a fleeting reminder of the values that bred 18th-century art, even if a retiree couldn’t refrain from chasing after the musicians to take pictures with her digital camera.

 legal and business issues for the performing arts, visit ggartslaw.com
legal and business issues for the performing arts, visit ggartslaw.com







 -Few professional orchestras enjoy the same degree of artistic adventure as the SFSYO. The orchestra came to Berlin as part of a European tour (June 20-July 6)—its eighth since being founded in 1981—that traveled through three other German cities, Luxemburg, and ended in Salzburg. As the orchestra’s Director of Education Ronald Gallman pointed out, playing on the same stage as the Berlin Philharmonic is already an enormous accomplishment, not to mention a huge boost for the morale. The ensemble, drawing together Bay area musicians aged 12 to 21, exists on a tuition-free basis (thanks to generous sponsorship which also made this year’s tour possible) and receives weekly coaching with members of the San Francisco Symphony as well as yearly sessions with San Francisco Symphony Music Director Michael Tilson Thomas. Guest artists have included Yo-Yo Ma, Sir Simon Rattle, John Adams, and Midori.
-Few professional orchestras enjoy the same degree of artistic adventure as the SFSYO. The orchestra came to Berlin as part of a European tour (June 20-July 6)—its eighth since being founded in 1981—that traveled through three other German cities, Luxemburg, and ended in Salzburg. As the orchestra’s Director of Education Ronald Gallman pointed out, playing on the same stage as the Berlin Philharmonic is already an enormous accomplishment, not to mention a huge boost for the morale. The ensemble, drawing together Bay area musicians aged 12 to 21, exists on a tuition-free basis (thanks to generous sponsorship which also made this year’s tour possible) and receives weekly coaching with members of the San Francisco Symphony as well as yearly sessions with San Francisco Symphony Music Director Michael Tilson Thomas. Guest artists have included Yo-Yo Ma, Sir Simon Rattle, John Adams, and Midori.-Jeff-Bartee.jpg?width=4256&height=2832&ext=.jpg)

